CLODROLIP = Liposomal drug preparations containing clodronate (Dichloromethylene bisphosphonic acid) are widely being used for the
in vivo depletion of macrophages in mammals for immunological studies.
Clodronate is encapsulated into homogeneous and stable small unilamellar liposomes of mean diameters between 130 and 150 nm. Encapsulation efficiency is 30% resulting in liposomes containing 18 ±2 mg/ml encapsulated clodronate. Immunohistology (Figure, right) shows the highly effective depletion of tumor associated macrophages using the F 4/80 macrophage marker following treatment of tumor bearing mice with
CLODROLIP.
CLODROLIP formulations deplete macrophages very effectively and are of high stability. In contrast to other clodronate-liposome formulations
CLODROLIP is a significantly improved formulation that can be stored at -80° C for more than one year without loss of depletion activity. The reagent is optimally suited for repetitive, long-term macrophage depletion experiments.
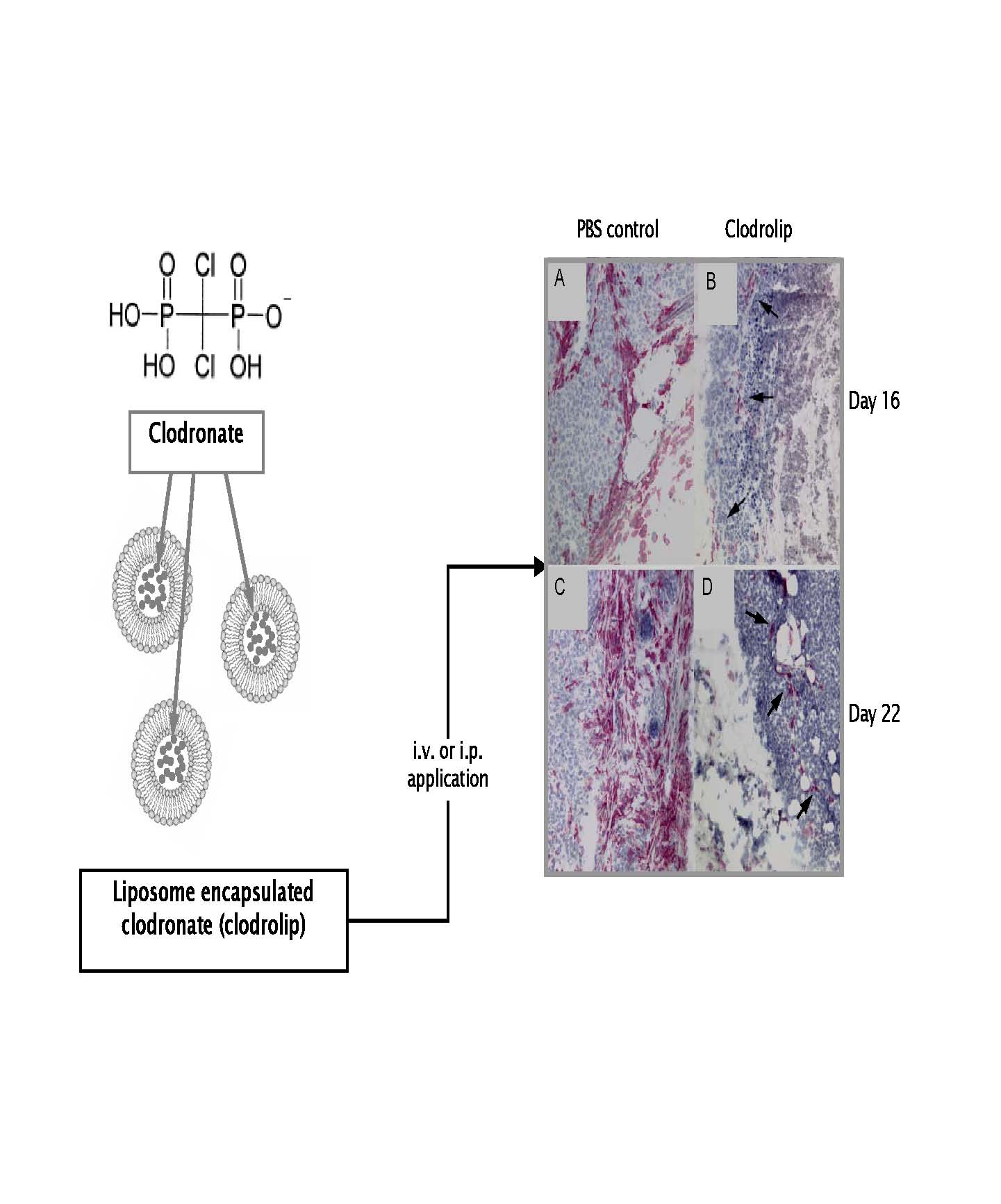
In the figure above CLODROLIP structure and demonstration of macrophage depletion efficiency in A673 rhabdomyosarcoma tumors
(red stained cells are F 4/80+ TAMs) are shown. TAM depletion is >95% (modified from Br. J. Cancer 95: 272, 2006)
The following figure shows the characteristics of macrophage depletion in the spleen after i.p. treatment with
CLODROLIP. Splenic macrophages (red pulp, marginal zone and metallophilic) are fully depleted by
CLODROLIP (panels S, T and U), whereas free clodronate has no effect (panels J, K, L and O, P). CD11b
+ macrophages and CD11c
+ dendritic cells are also depleted but at a lesser extent (panels X and Y). Follicular dendritic cells (FDC), B and T cells are not affected. Interestingly, CD68
+ macrophages are not depleted in the spleen of healthy mice (panels D, M and V) or in tumors of tumor bearing mice (see Br. J. Cancer 95: 272, 2006).
Immunohistochemical stains of spleen sections obtained from mice injected with PBS (A to I), with free clodronate (J to R), or with Clodrolip (S to A1):
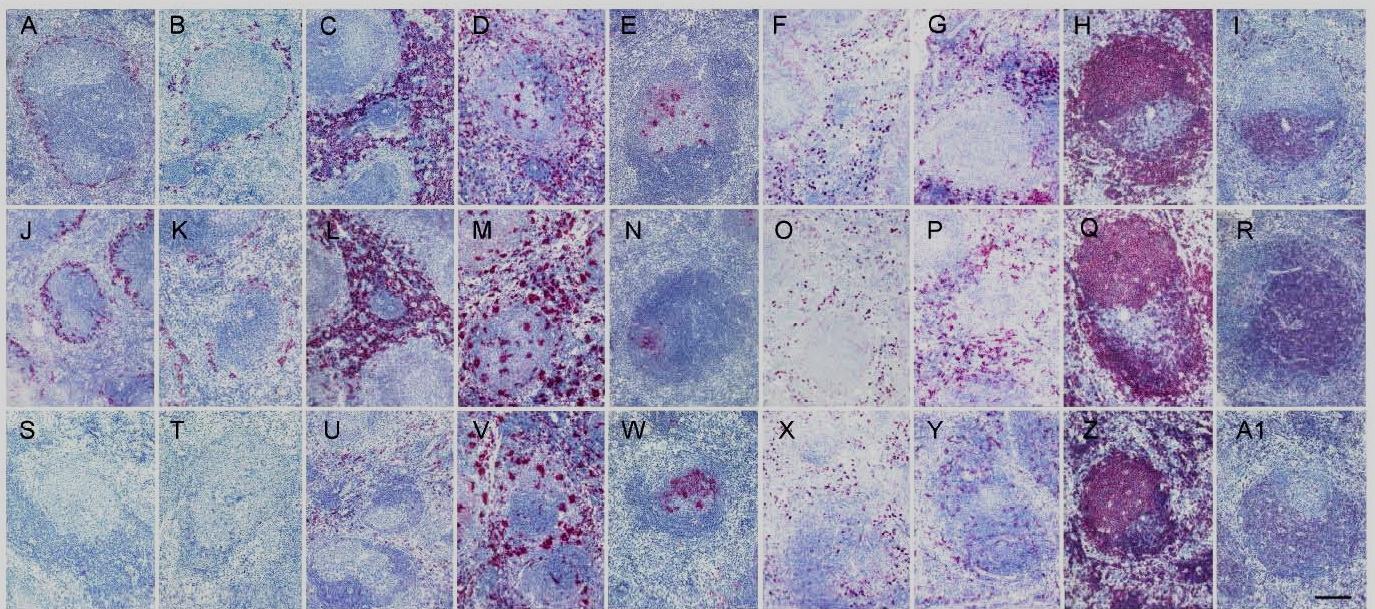
A, J, and S - marginal zone metallophilic MOMA1+ macrophages. B, K, and T - marginal zone ER-TR 9+ macrophages. C, L, and U -red pulp F4/80+ macrophages. D, M and V - red and white pulp CD 68+ macrophages. E, N, and W - white pulp FDC+ dendritic cells. F, O and X - red pulp CD11b+ macrophages. G, P and Y - red pulp CD11c+ dendritic cells. H, Q, and Z- white pulp B220+ B-cells. I, R and A1 - white pulp CD3+ T-cells. Bar indicates 0.100 mm.
Here you find PubMed links to recent publications where macrophage depletion was successfully performed using CLODROLIP formulations:
Sequential Activation of Two Pathogen-Sensing Pathways Required for Type I Interferon Expression and Resistance to an Acute DNA Virus Infection. Xu RH, Wong EB, Rubio D, Roscoe F, Ma X, Nair S, Remakus S, Schwendener R, John S, Shlomchik M, Sigal LJ.
Immunity 43(6):1148-59, 2015.
Inhibition of Cyclooxygenase-2 Prevents Chronic and Recurrent Cystitis. Hannan TJ, Roberts PL, Riehl TE, van der Post S, Binkley JM, Schwartz DJ, Miyoshi H, Mack M, Schwendener RA, Hooton TM, Stappenbeck TS, Hansson GC, Stenson WF, Colonna M, Stapleton AE, Hultgren SJ.
eBioMedicine 1, p46-57, 2014.
Depletion of cutaneous macrophages and dendritic cells promotes growth of Basal Cell Carcinoma in mice.
Koenig S, Nitzki F, Uhmann A, Dittmann K, Theiss-Suennemann J, Herrmann M, Reichardt HM, Schwendener R, Pukrop T, Schulz-Schaeffer W, Hahn H.
PLoS One 9(4):e93555, 2014.
Embryonic and adult-derived resident cardiac macrophages are maintained through distinct mechanisms at steady state and during inflammation.
Epelman S, Lavine KJ, Beaudin AE, Sojka DK, Carrero JA, Calderon B, Brija T, Gautier EL, Ivanov S, Satpathy AT, Schilling JD, Schwendener R, Sergin I, Razani B, Forsberg EC, Yokoyama WM, Unanue ER, Colonna M, Randolph GJ, Mann DL.
Immunity. 40(1):91-104, 2014.
Macrophage and T cell produced IL-10 promotes viral chronicity. Richter K, Perriard G, Behrendt R, Schwendener RA, Sexl V, Dunn R, Kamanaka M, Flavell RA, Roers A, Oxenius A.
PLoS Pathog. 9(11):e1003735,2013.
Microparticles released by Listeria monocytogenes-infected macrophages are required for dendritic cell-elicited protective immunity.
Zhang Y, Zhang R, Zhang H, Liu J, Yang Z, Xu P, Cai W, Lu G, Cui M, Schwendener RA, Shi HZ, Xiong H, Huang B.
Cell Mol Immunol. 9: 489, 2012.
Inhibition of the Kit ligand/c-Kit axis attenuates metastasis in a mouse model mimicking local breast cancer relapse after radiotherapy. Kuonen F, Laurent J, Secondini C, Lorusso G, Stehle JC, Rausch T, Faes-Van't Hull E, Bieler G, Alghisi GC, Schwendener R, Andrejevic-Blant S, Mirimanoff RO, Ruegg C.
Clin Cancer Res. 18(16):4365-4374, 2012.
Radiotherapy promotes tumor-specific effector CD8+ T cells via dendritic cell activation. Gupta A, Probst HC, Vuong V, Landshammer A, Muth S, Yagita H, Schwendener R, Pruschy M, Knuth A, van den Broek M.
J Immunol. 189(2):558-66, 2012.
Epoxyeicosanoids stimulate multiorgan metastasis and tumor dormancy escape in mice. Panigrahy D, Edin ML, Lee CR, Huang S, Bielenberg DR, Butterfield CE, Barnés CM, Mammoto A, Mammoto T, Luria A, Benny O, Chaponis DM, Dudley AC, Greene ER, Vergilio JA, Pietramaggiori G, Scherer-Pietramaggiori SS, Short SM, Seth M, Lih FB, Tomer KB, Yang J, Schwendener RA, Hammock BD, Falck JR, Manthati VL, Ingber DE, Kaipainen A, D'Amore PA, Kieran MW, Zeldin DC.
J Clin Invest. 122(1):178-91, 2012.
S100A7 enhances mammary tumorigenesis through upregulation of inflammatory pathways. Nasser MW, Qamri Z, Deol YS, Ravi J, Powell CA, Trikha P, Schwendener RA, Bai XF, Shilo K, Zou X, Leone G, Wolf R, Yuspa SH, Ganju RK.
Cancer Res. 72(3):604-15, 2012.
Inflammation is necessary for long-term but not short-term high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance. Lee YS, Li P, Huh JY, Hwang IJ, Lu M, Kim JI, Ham M, Talukdar S, Chen A, Lu WJ, Bandyopadhyay GK, Schwendener R, Olefsky J, Kim JB.
Diabetes 60:2474-2483, 2011.
CD11c+ Dendritic cells and B cells contribute to the tumoricidal activity of anti-DR5 antibody therapy in established tumors. Haynes NM, Hawkins ED, Li M, McLaughlin NM, Hämmerling GJ, Schwendener R, Winoto A, Wensky A, Yagita H,Takeda K, Kershaw MH, Darcy PK, Smyth MJ.
J Immunol. 185(1):532-41, 2010.
In vivo bioluminescence imaging and histopathopathologic analysis reveal distinct roles for resident and recruited immune effector cells in defense against invasive aspergillosis. Ibrahim-Granet O, Jouvion G, Hohl TM, Droin-Bergere S, Philippart F, Kim OY, Adib-Conquy M, Schwendener R, Cavaillon JM, Brock M.
BMC Microbiol. 10(1):105, 2010.
Identification of a subpopulation of macrophages in mammary tumor-bearing mice that are neither M1 nor M2 and are less differentiated. Torroella-Kouri M, Silvera R, Rodriguez D, Caso R, Shatry A, Opiela S, Ilkovitch D, Schwendener RA, Iragavarapu-Charyulu V, Cardentey Y, Strbo N, Lopez DM.
Cancer Res. 69: 4800-09, 2009.
Critical role of CD11b+ macrophages and VEGF in inflammatory lymphangiogenesis, antigen clearance, and inflammation resolution. Kataru RP, Jung K, Jang C, Yang H, Schwendener RA, Baik JE, Han SH, Alitalo K, Koh GY.
Blood 113: 5650-59, 2009.
A pro-inflammatory signature mediates FGF2-induced angiogenesis. Andrés G, Leali D, Mitola S, Coltrini D, Camozzi M, Corsini M, Belleri M, Hirsch E, Schwendener RA, Christofori G, Alcami A, Presta M.
J. Cell. Mol. Med. 13(8b): 2083-2108, 2009.
Gene transfer may be preventive but not curative for a lysosomal transport disorder. Hippert C, Dubois G, Morin C, Disson O, Ibanes S, Jacquet C, Schwendener R, Antignac C, Kremer EJ, Kalatzis V.
Mol Ther. 16(8):1372-81, 2008.
Persistent activation of an innate immune response translates respiratory viral infection into chronic lung disease. Kim EY, Battaile JT, Patel AC, You Y, Agapov E, Grayson MH, Benoit LA, Byers DE, Alevy Y, Tucker J, Swanson S, Tidwell R, Tyner JW, Morton JD, Castro M, Polineni D, Patterson GA, Schwendener RA, Allard JD, Peltz G, Holtzman MJ.
Nat. Med. 14(6):633-40, 2008.
Profound but dysfunctional lymphangiogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor ligands from CD11b+ macrophages in advanced ovarian cancer. Jeon BH, Jang C, Han J, Kataru RP, Piao L, Jung K, Cha HJ, Schwendener RA, Jang KY, Kim KS, Alitalo K, Koh GY.
Cancer Res. 68(4):1100-1109, 2008.
Angiogenic role of LYVE-1-positive macrophages in adipose tissue. Cho CH, Koh YJ, Han J, Sung HK, Jong Lee H, Morisada T, Schwendener RA, Brekken RA, Kang G, Oike Y, Choi TS, Suda T, Yoo OJ, Koh GY.
Circ. Res. 100(4):e47-57, 2007.
CCL5-CCR5 interaction provides antiapoptotic signals for macrophage survival during viral
infection. Tyner JW, Uchida O, Kajiwara N, Kim EY, Patel AC, O'sullivan MP, Walter MJ,
Schwendener RA, Cook DN, Danoff TM, Holtzman MJ.
Nat. Med. 11:1180-1187, 2005.
Pulmonary aspiration: New therapeutic approaches in the experimental model. Beck-Schimmer
B, Rosenberger DS, Neff SB, Jamnicki M, Suter D, Fuhrer T, Schwendener R, Booy C, Reyes L,
Pasch T, Schimmer RC.
Anesthesiology 103(3):556-566, 2005.
Decreased alveolar oxygen induces lung inflammation. Madjdpour C, Jewell UR, Kneller S,
Ziegler U, Schwendener RA, Booy C, Klausli L, Pasch T, Schimmer RC, Beck-Schimmer B.
Am.J.
Physiol.Lung Cell Mol.Physiol. 284(2):L360-7, 2003.
Macrophage Links:

